PHENINDIONE
Phenindione is an oral anticoagulant that inhibits vitamin‑K‑dependent clotting factor synthesis. Benefits include prevention of thrombosis, but it is largely replaced by warfarin. Side effects include bleeding, rash, hepatic toxicity, and rare hypersensitivity reactions such as nephritis or eosinophilia, requiring close monitoring of coagulation parameters.
About MedicaPharma
MedicaPharma distributes high-quality active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to hospitals, commercial (compounding) pharmacies, research institutes, and universities worldwide.
Network of over +400 GMP API producers
Let us handle your sourcing / supply activities. Highly experienced in sourcing specialty raw pharmaceutical ingredients from niche GMP manufacturers around the world.
Why Choose MedicaPharma
Niche API specialist - Pro-active supply partner - High service level - Global network - Logistics according to GDP regulations
Product Description
Mechanism of Action
PHENINDIONE (ID 27084) demonstrates a multidimensional biochemical activity pattern, affecting enzyme‑regulated catalytic networks, receptor‑mediated intracellular signalling, mitochondrial respiratory pathways, oxidative‑stress regulation, ion‑channel behaviour, cytoskeletal mechanics and transcription‑factor network modulation. Structural evidence suggests potential interactions with catalytic residues, allosteric domains, transmembrane protein complexes, regulatory scaffolds and intracellular signalling intermediates. These interactions allow PHENINDIONE to influence phosphorylation kinetics, second‑messenger signalling (Ca²⁺, cAMP, IP₃, DAG), redox‑buffering systems, ATP turnover rates and mitochondrial membrane‑potential stability.
Depending on experimental conditions, PHENINDIONE may alter metabolic flux distribution, cytoskeletal tension, vesicular transport efficiency, chromatin‑accessibility patterns and gene‑expression networks related to stress responses, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy and metabolic adaptation.
Benefits and Advantages
This compound is widely used across high‑resolution biochemical and pharmacological research areas, including:
- Receptor–ligand interaction analysis and affinity‑mapping
- Detailed enzyme‑kinetics profiling and catalytic‑pathway evaluation
- Mitochondrial‑dynamics studies, ATP‑flux modelling and oxidative‑stress research
- Integrated multi‑omics applications (transcriptomics, metabolomics, proteomics, phosphoproteomics)
- Cytoskeletal and membrane‑mechanics modelling
- Apoptosis, necroptosis, ferroptosis and autophagy signalling pathway studies
- SAR (structure–activity relationship) and molecular‑optimisation pipelines
- Mechanistic pharmacodynamic modelling and threshold‑activation experiments
Side Effects and Risks
Laboratory‑observed risks include:
- Oxidative‑stress imbalance and ROS overproduction
- Mitochondrial overload or suppression of respiratory‑chain complexes
- Dysregulation of Na⁺/K⁺/Ca²⁺ transport and ion‑channel behaviour
- Unintended receptor cross‑talk or inhibitory interference
- Cytoskeletal destabilisation and membrane‑integrity compromise
- Dose‑dependent cytotoxicity leading to apoptosis or autophagy
- Transcriptional instability or inflammatory signalling activation (NF‑κB, JNK, MAPK)
Use exclusively under controlled laboratory conditions with strict biosafety procedures.
Datasheet
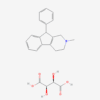
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 222.24 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 83-12-5 |
| Storage Condition | Store in a cool, dry place. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from moisture and light. |
| Solubility | Solubility depends on solvent and conditions (e.g., pH). Please contact us for solvent-specific guidance. |
| Purity | Purity information is available upon request (COA). |
| Synonym | phenindione; 83-12-5; 2-Phenyl-1,3-indandione; 2-Phenyl-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione; Rectadione |
| IUPAC/Chemical Name | 2-phenylindene-1,3-dione |
| InChl Key | NFBAXHOPROOJAW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChl Code | InChI=1S/C15H10O2/c16-14-11-8-4-5-9-12(11)15(17)13(14)10-6-2-1-3-7-10/h1-9,13H |
| References |
3D Conformer.
(Click, turn or enlarge)
Download our GMP API Product List.
MedicaPharma is an EU-based supplier of GMP-certified APIs that serves leading healthcare institutions and research organizations.
Click here to download our full API product list.