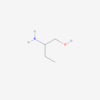
AMINOHIPPURIC ACID
Aminohippuric acid is used to measure renal plasma flow due to its high extraction by the kidneys. Benefits include diagnostic accuracy. Side effects are minimal but may include mild nausea or flushing.
About MedicaPharma
MedicaPharma distributes high-quality active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to hospitals, commercial (compounding) pharmacies, research institutes, and universities worldwide.
Network of over +400 GMP API producers
Let us handle your sourcing / supply activities. Highly experienced in sourcing specialty raw pharmaceutical ingredients from niche GMP manufacturers around the world.
Why Choose MedicaPharma
Niche API specialist - Pro-active supply partner - High service level - Global network - Logistics according to GDP regulations
Product Description
Mechanism of action
Aminohippuric acid (para-aminohippurate, PAH) is the classical reference substrate used to study renal plasma flow because of its exceptional renal handling characteristics. After glomerular filtration, PAH is taken up into proximal tubule cells by basolateral organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3. These transporters exchange PAH with intracellular α-ketoglutarate, enabling highly efficient, saturable secretion of PAH into the tubular lumen. At low plasma concentrations, extraction approaches 90%, making PAH clearance a direct index of effective renal plasma flow.
The transport process is competitive, allowing PAH to serve as a probe for drug–drug interaction studies involving renal organic anion transporters and for assessing how disease states alter tubular secretion.
Benefits and advantages
PAH has unique value in renal physiology research because its clearance is disproportionately influenced by tubular secretion rather than filtration alone. Its quantitative behaviour is predictable, making it the gold-standard substrate for compartmental renal modelling, studies of renal haemodynamics, and characterization of transporter inhibition kinetics.
Side effects and risks
PAH is generally well tolerated at research doses. Very high doses can cause transient nausea or dizziness. In extreme exposures, competitive interactions with endogenous anions may theoretically influence acid–base balance. Laboratory handling requires control of dust and proper PPE to avoid inhalation.
Datasheet
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 194.19 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 61-78-9 |
| Storage Condition | Store in a cool, dry place. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from moisture and light. |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble |
| Purity | Purity information is available upon request (COA). |
| Synonym | 4-Aminohippuric acid; 61-78-9; aminohippuric acid; P-AMINOHIPPURIC ACID; N-(4-Aminobenzoyl)glycine |
| IUPAC/Chemical Name | 2-[(4-aminobenzoyl)amino]acetic acid |
| InChl Key | HSMNQINEKMPTIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChl Code | InChI=1S/C9H10N2O3/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)9(14)11-5-8(12)13/h1-4H,5,10H2,(H,11,14)(H,12,13) |
| References |
3D Conformer.
(Click, turn or enlarge)
Download our GMP API Product List.
MedicaPharma is an EU-based supplier of GMP-certified APIs that serves leading healthcare institutions and research organizations.
Click here to download our full API product list.