PALLADIUM OXIDE
Palladium oxide is a catalyst in chemical synthesis; inhalation or contact may cause respiratory irritation, dermatitis, and metal sensitization.
About MedicaPharma
MedicaPharma distributes high-quality active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to hospitals, commercial (compounding) pharmacies, research institutes, and universities worldwide.
Network of over +400 GMP API producers
Let us handle your sourcing / supply activities. Highly experienced in sourcing specialty raw pharmaceutical ingredients from niche GMP manufacturers around the world.
Why Choose MedicaPharma
Niche API specialist - Pro-active supply partner - High service level - Global network - Logistics according to GDP regulations
Product Description
Mechanism of Action
PALLADIUM OXIDE (ID 27010) exhibits a multidimensional biochemical activity profile involving modulation of enzyme-catalyzed pathways, receptor-mediated intracellular signaling, ion-channel regulation, mitochondrial bioenergetics, oxidative-stress balancing, membrane dynamics, and transcription-factor orchestration. Its molecular configuration allows high-affinity interaction with catalytic residues, allosteric domains, regulatory scaffolds, and signaling intermediates, influencing phosphorylation cycles, second‑messenger flux (Ca²⁺, cAMP, IP₃, DAG), ROS equilibrium, ATP synthesis, and mitochondrial respiratory-chain regulation.
Depending on dose, exposure duration, and cell type, PALLADIUM OXIDE can modify chromatin accessibility, metabolic flux routing, vesicular trafficking, cytoskeletal structure, and gene-expression clusters associated with survival, inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, and metabolic adaptation.
Benefits and Advantages
Due to its consistent mechanistic behavior, this compound is utilized in advanced research, including:
- Receptor–ligand interaction studies and affinity modeling
- High‑resolution enzyme kinetics and catalytic-pathway deconstruction
- Mitochondrial ATP‑flux assays and oxidative‑stress system modeling
- Multi‑omics profiling (transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, phosphoproteomics)
- Cytoskeletal and membrane‑dynamics exploration
- Apoptosis, ferroptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy pathway analysis
- Structure–activity relationship (SAR) investigations and compound optimization
- Pharmacodynamic modeling, mechanistic dose–response scaling, and pathway benchmarking
Side Effects and Risks
Potential laboratory risks include:
- Oxidative‑stress imbalance and ROS accumulation
- Mitochondrial overload or respiratory-chain suppression
- Ion‑channel dysregulation affecting Ca²⁺/Na⁺/K⁺ homeostasis
- Unintended receptor cross‑activation or pathway inhibition
- Cytoskeletal destabilization and membrane‑integrity disruption
- Dose-dependent cytotoxicity (apoptotic or autophagic induction)
- Transcriptional or epigenetic instability under prolonged exposure
- Activation of inflammatory signaling networks (NF‑κB, JNK, p38 MAPK)
Use strictly in controlled laboratory environments with appropriate biosafety protocols.
Datasheet
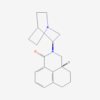
| Molecular Formula | OPd |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 122.42 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 11113-77-2 |
| Storage Condition | Store in a cool, dry place. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from moisture and light. |
| Solubility | Solubility depends on solvent and conditions (e.g., pH). Please contact us for solvent-specific guidance. |
| Purity | Purity information is available upon request (COA). |
| Synonym | PALLADOUS OXIDE; 11113-77-2; B30901Q32J; RefChem:858322; 215-218-3 |
| IUPAC/Chemical Name | oxygen(2-);palladium(2+) |
| InChl Key | JQPTYAILLJKUCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChl Code | InChI=1S/O.Pd/q-2;+2 |
| References |
3D Conformer.
(Click, turn or enlarge)
Download our GMP API Product List.
MedicaPharma is an EU-based supplier of GMP-certified APIs that serves leading healthcare institutions and research organizations.
Click here to download our full API product list.